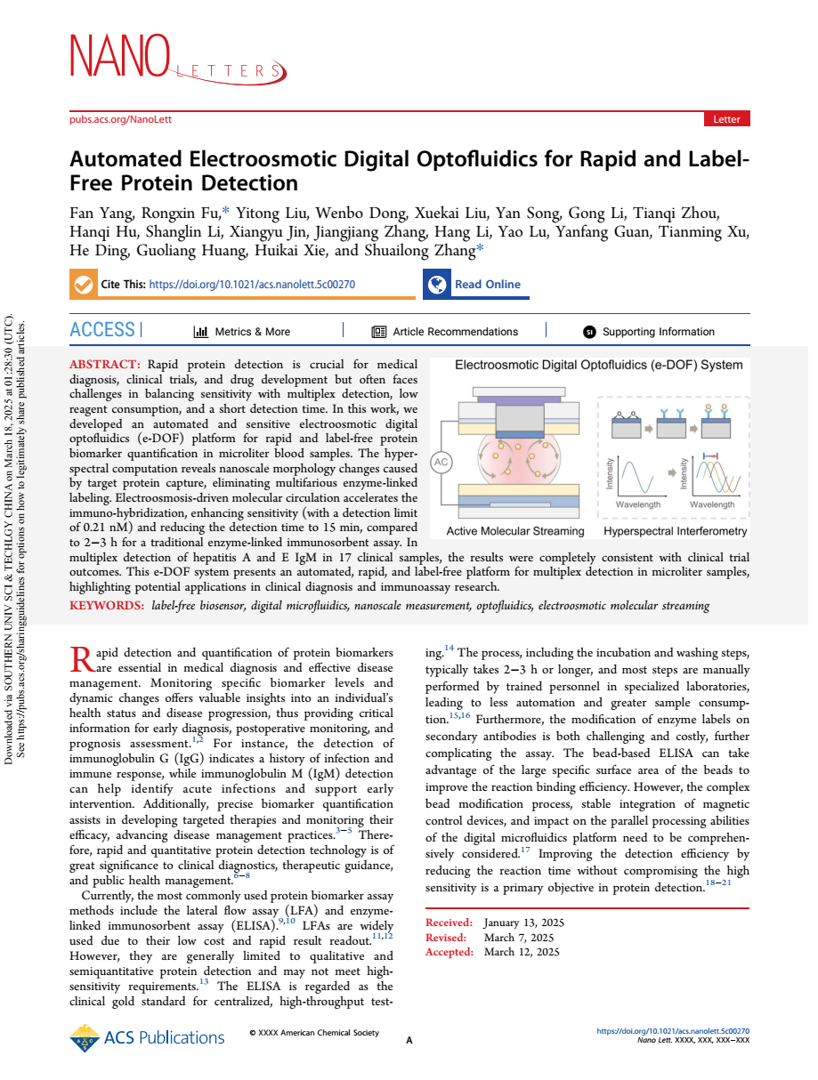
A multidisciplinary team from Beijing Institute of Technology, University of Toronto, and other institutions has published groundbreaking research titled "Automated Electroosmotic Digital Optofluidics for Rapid and Label-Free Protein Detection" in Nano Letters.
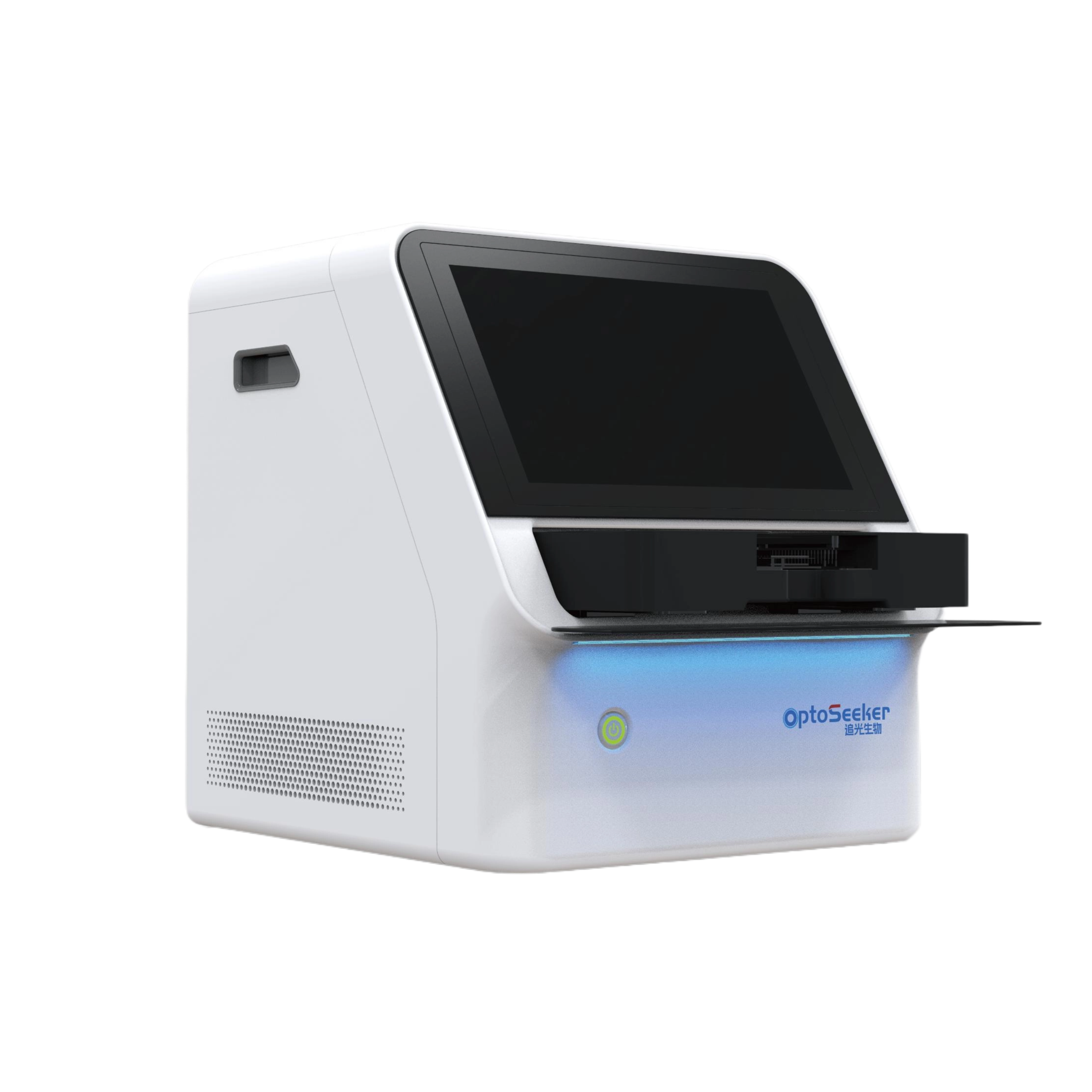
As a key technical partner, Optoseeker contributed to digital microfluidic chip design and validation protocols, supported fluorescence tracing experiments using its DropletBot®Digital Microfluidics Platform, and was acknowledged in the paper.
The team developed an electroosmotic digital optofluidics (e-DOF) platform that quantifies protein-binding-induced nanoscale deformations via hyperspectral interferometric computation. By integrating electroosmosis-driven molecular self-circulation technology, the detection time was slashed from 2–3 hours (traditional ELISA) to 15 minutes, achieving a sensitivity of 0.21 nM (>50× more sensitive than ELISA) and 100% accuracy in clinical samples.
I. Journal Profile
Nano Letters (American Chemical Society) is a top-tier journal renowned for pioneering high-impact research at the intersection of nanotechnology and biomedicine. Key metrics:
- Impact Factor (2024): 9.6
- JCR Quartile: Q1
- CAS Rating: Materials Science, Tier 1
II. Research Highlights
1. Label-Free Ultrasensitive Detection
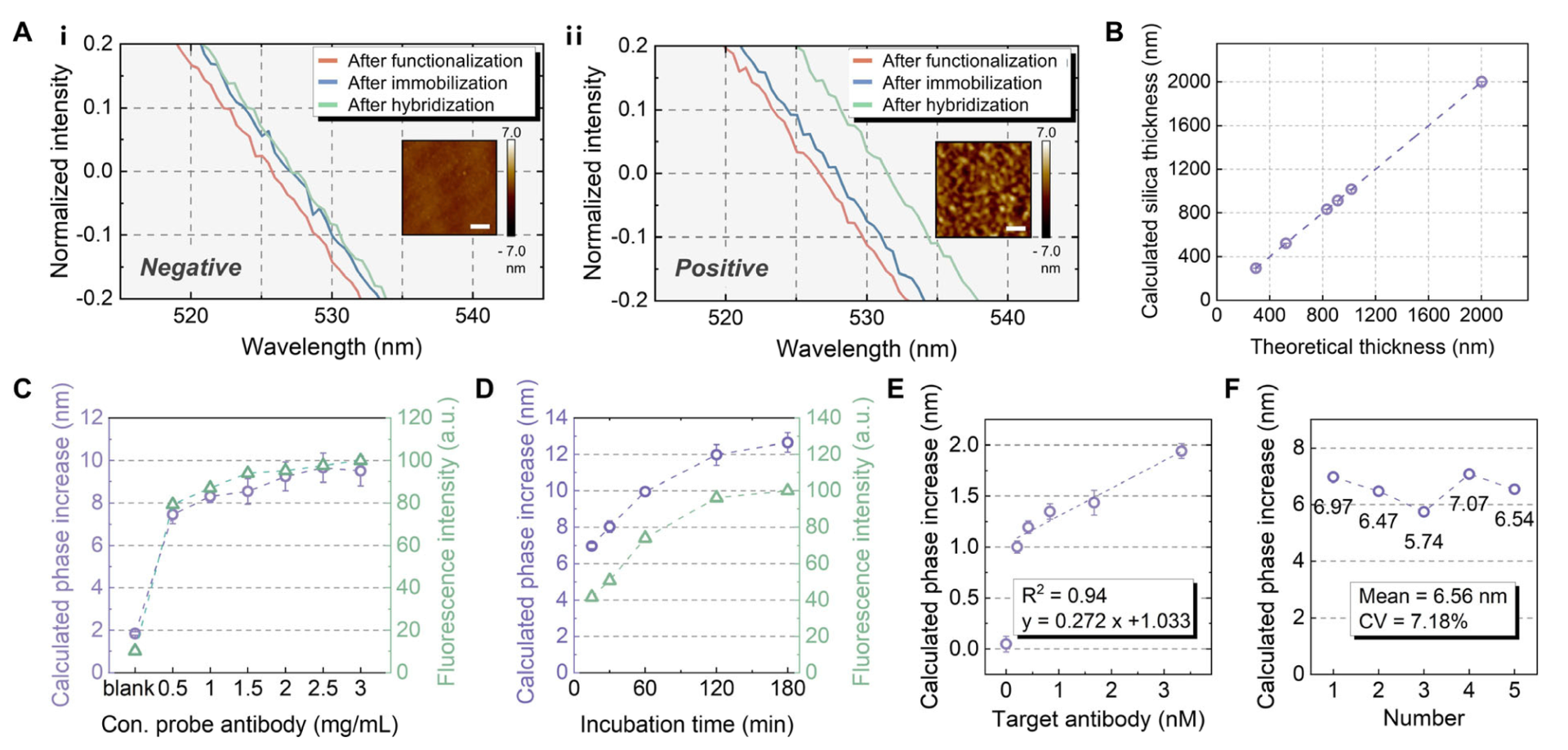
Characterization, optimization, and validation data
- Innovation: First e-DOF platform combining hyperspectral interferometry to directly quantify protein-binding nanoscale deformations.
- Performance: Detection limit of 0.21 nM (50× more sensitive than ELISA), no enzymatic labeling required.
2. Electroosmotic Molecular Flow Acceleration
- Technology: Electroosmosis-driven self-circulation accelerates probe-protein binding in 4 μL samples.
- Result: Detection completed in 15 minutes (vs. ELISA’s 2–3 hrs) with 100% clinical accuracy.
(Fig. 3: Microfluidic droplet circulation dynamics)
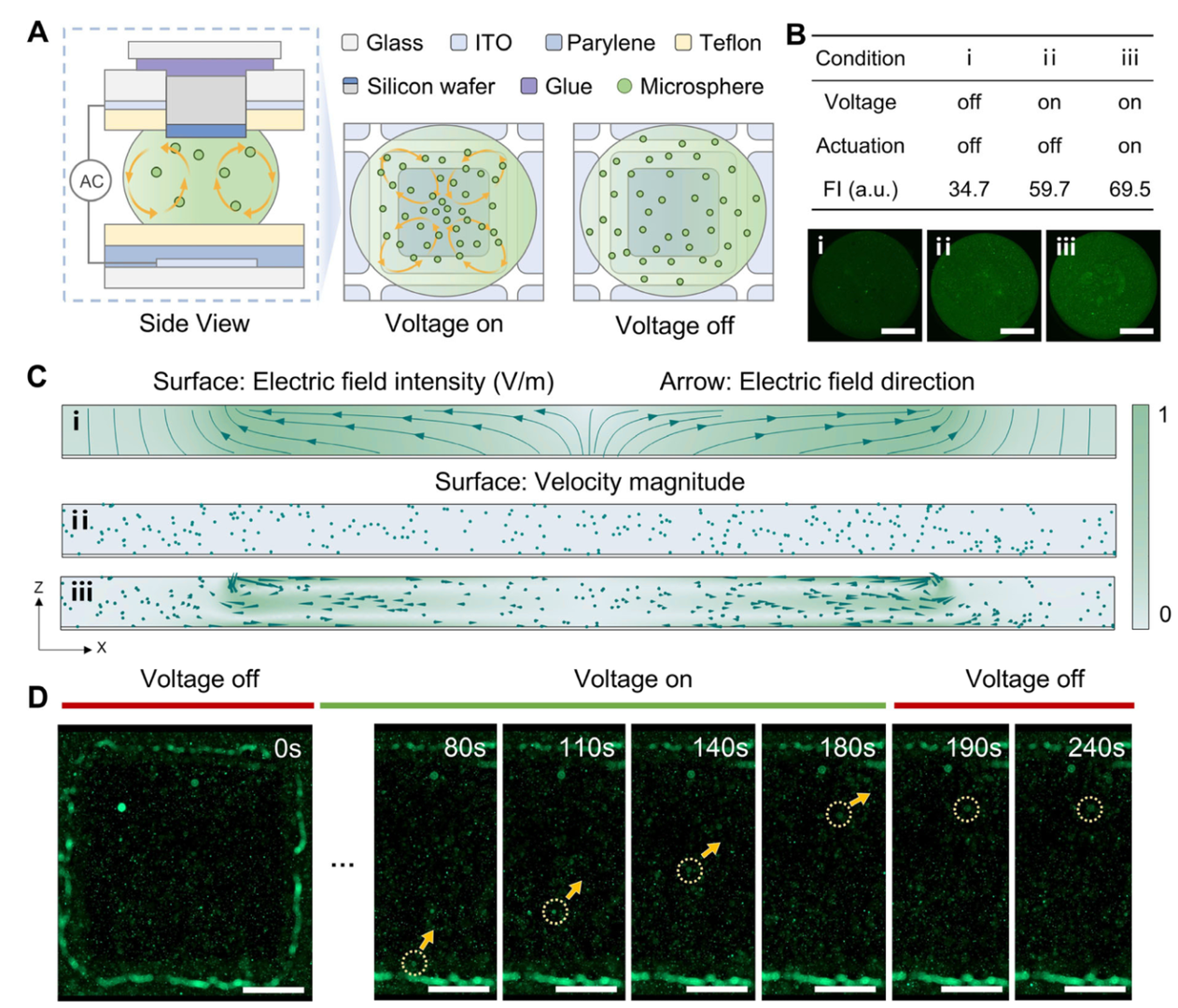
3. Fully Automated Integrated Platform
- Design: Combines digital microfluidic chips with optical supercomputing modules.
- Workflow: Fully automated sample separation-reaction-wash-detection; supports multiplex detection (e.g., HAV/HEV IgM) for point-of-care testing (POCT).
(Fig. 4: On-chip detection performance)
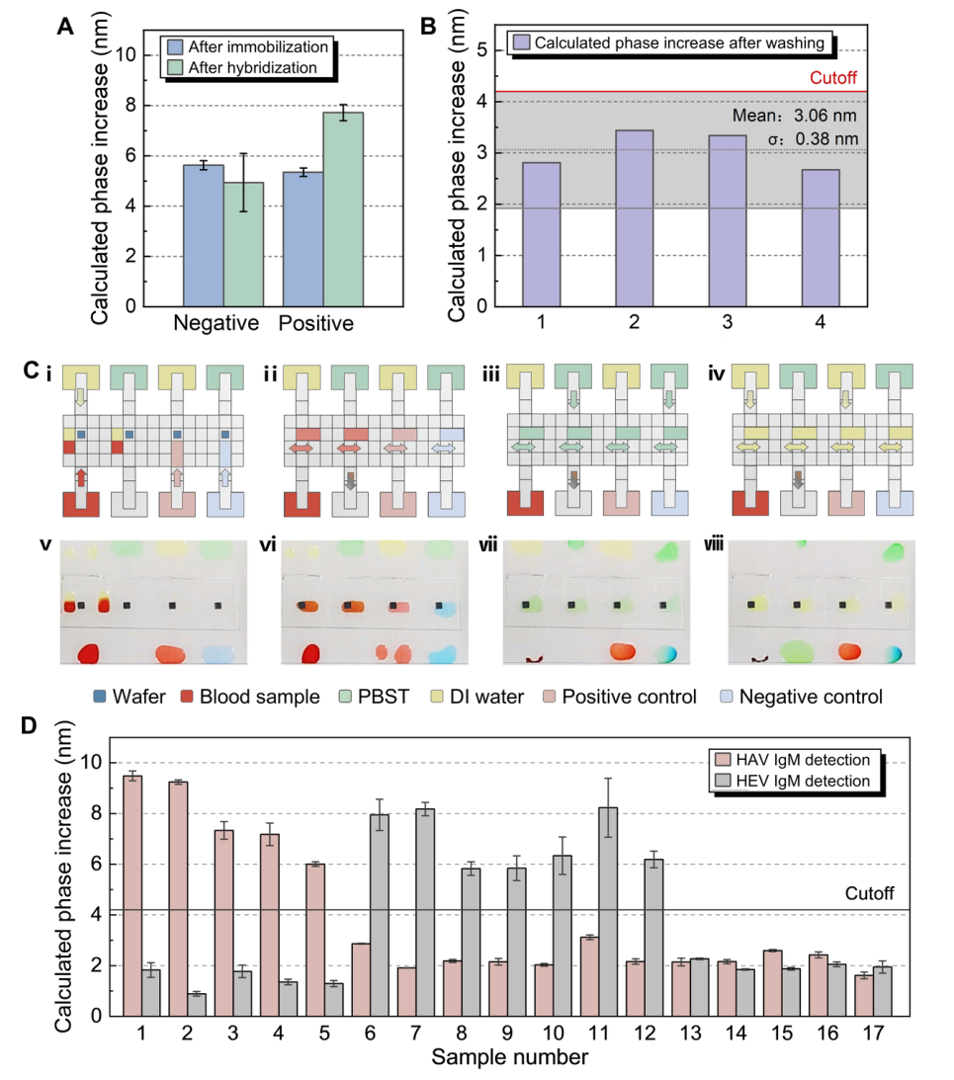
Applications
This technology holds transformative potential for:
- Early disease screening (e.g., Hepatitis A/E)
- Personalized medicine
- Clinical diagnostics
Compared to ELISA, e-DOF drastically reduces sample volume and detection time, enabling rapid, label-free, multiplexed detection.
Core Equipment Support
The study deployed Optoseeker’s DropletBot® Digital Microfluidics System to achieve unprecedented detection efficiency and sensitivity. This innovation promises broad applications in disease diagnostics, drug development, and POCT, delivering transformative solutions for clinical practice.